MongoDB and MySQL are two of the famous names when we talk about Databases.
Database, is a critical part of every project and mobile app. Businesses deal with data from several sources, whether from internal sources like employee details or external sources like end user details. All the necessary data needs to be stored in single or multiple databases so that it can be feched according to the requirements with accuracy.
Digging further, relational data and non-relational databases are the most popular database types. And, with the availability of a number of relational and non-relational databases, businesses are highly confused between MongoDB and MySQL databases.
In this article, we will compare MongoDB and MySQL to assist entrepreneurs and enterprises in deciding which Database they should use.
Table of Contents
MongoDB vs MySQL, let the battle begin
We will consider several factors to compare both databases. From all these pointers, we will prepare a conclusion for you so you can finally choose the best choice for business between MongoDB and MySQL.
MongoDB and MySQL: What are they?
We will start the comparison by understanding MongoDB and MySQL briefly to move further to the complex differences.
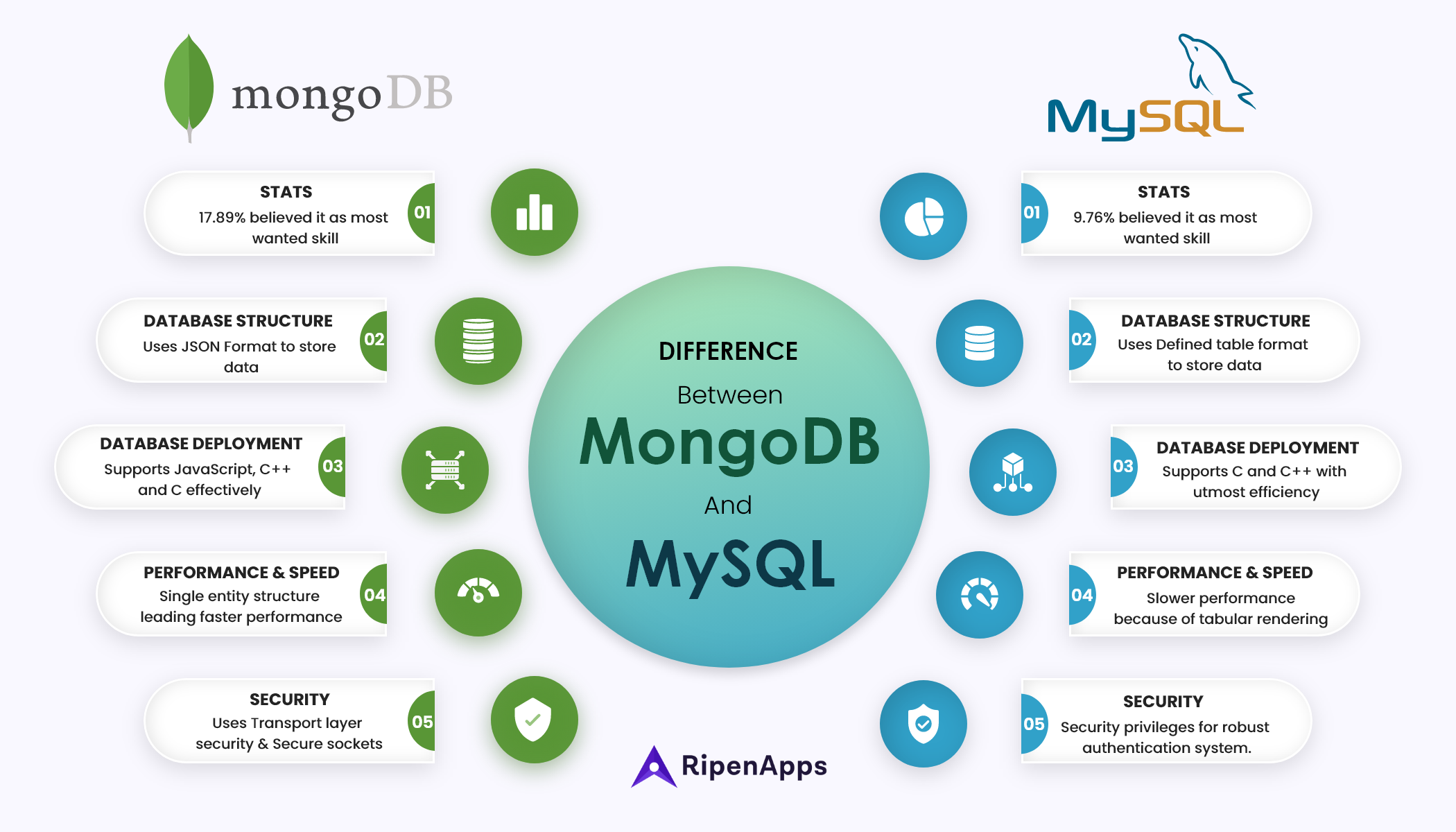
In non-relational databases, MongoDB has gained a strong place since its first release in 2010. MongoDB introduced a modern way of data storing format, JSON. Enterprises used MongoDB when there was no connection between different sets of data. Meaning there was no need to create a relationship between multiple tables. Businesses can easily create or add new fields without affecting other collections. Database administrators found MongoDB to be very simple and elegant to use, enhancing the productivity of the business.
An open-source database highly used to satisfy relational database needs; MySQL is owned by Oracle corporation. The users using MySQL can define the relationship between different data tables and establish rules according to their requirements. The majority of organizations use MySQL databases to manage their complex data.
In the most wanted database skills among software developers worldwide in 2021, MongoDB scored 17.89& and MySQL scored 9.76%.
Database structure: MongoDB vs. MySQL
Every Database has a database structure, the building block on which it was created. You can understand it as the visual representation displaying the relational or non-relational trait of a database. Let us compare the Database structure for MongoDB and MySQL.
MongoDB stores data in JSON format with diverse structures. It has the potential to store related data sets together, but you have to use MongoDB query language to perform operations on the data sets.
When we look at MySQL, the values of data are stored in the defined tables by the database structure of MySQL. SQL is used to access the database structure of MySQL, where the database structure is defined by Schema. The rows and table have identical structures.
Index Optimization: MongoDB vs MySQL
This is one of the similar pointers between MongoDB and MySQL since both of them use indexing to perform the data search operation. But there is a difference in approach between the two.
In MongoDB. When the index is not found, it goes through each and every collection of documents to match the query statement.
Whereas in MySQL, when the case is undefined, the Database scans all the tables to match the query with existing rows.
Deployment of Database: MongoDB vs MySQL
You can write MongoDB databases with popular languages like JavaScript, C++, and C. The binaries are available for multiple platforms like Linux, Windows, and OS X, and you can choose anyone depending upon your requirements and usage.
On the other hand, MySQL databases can be written in C and C++ language. The platforms it supports are wider than MongoDB. You can use binaries for OS X, Linux, Windows, FreeBSD, AIX, NetBSD, and more, according to your choice.
Replication: MongoDB vs MySQL
With MongoDB, you can take the benefit of auto-elections support, build-in replications, and Sharding. Developers have powerful features like using auto-elections to setup a secondary database. A secondary Database is useful when your primary Database meets any kind of failure. With Sharding, you can perform horizontal scaling.
Coming to MySQL, you can take the benefit of master-slave and master-master replications, replicating multiple masters parallelly.
Company offerings: MongoDB vs MySQL
MongoDB leans more towards enterprise requirements. You can add on the support as per requirement at any point in time. And the company delivers regular and stable upgrades and updates.
Whereas with MySQL, Businesses and individual developers can take the benefit of Lifetime support from Oracle. Here are the plans:
- Sustain plan: Suited for businesses who are 9+ years old.
- Extended plan: Suited for businesses 6-8 years old.
- Premier plan: Businesses with 1-5 years old can be fir in the Premier plan.
With Oracle’s MySQL, you also have 24×7 tech support from the company with the latest updates and bug fixes.
Performance and Speed: MongoDB vs. MySQL
MongoDB can control massive volumes of data without any form of restriction. Why? Because it follows a single entity structure where all the data is stored in a single document. Users can read and write data with the great performance and speed of MongoDB.
MySQL, on the other hand, is slower than MongoDB in handling a massive amount of data. High volumes of unstructured data management are also slow with MySQL. The data renders in multiple tabular formats, which reduces the performance.
Security and Productivity: MongoDB vs. MySQL
MongoDB is strong with security features offering auditing and robust authentication and authorization. The transport layer security and secure sockets layer offer encryption of data. Developers can work productively with the JSON documents with fewer efforts.
MySQL follows security privileges to secure the database. The authenticated users are the only ones to perform operations with Data. And, the overall productivity is still slow since it follows the traditional table structure model.
Conclusion- MongoDB or MySQL, what to use?
MongoDB is highly recommended when your priorities are automation, fast speed and performance, and strong data recovery. It is best suited when your data is least relational in nature. Whereas MySQL is highly suitable when your data is highly relational with fixed schema and data structure. Security is another major matter since MySQL is more secure with privileged-based authentication. Keeping everything aside, there is no major winner in the comparison since both have different use cases and you are free to choose one according to your requirements.
Got queries or hiring MongoDB or MySQL experts for your app development project?
Connect with our sales team instantly to further discuss your project.
FAQ
Q: Should I choose MongoDB over MySQL?
MongoDB is an excellent choice if you target a modern database with real-time analytics, content management, and other flat operations. But you should go with MySQL if the database’s complexity is highly relational.
Q: Which database is faster, MongoDB or MySQL?
MongoDB is faster because it follows a modern JSON format to store the data. Whereas MySQL follows the traditional approach of tables, so it can be relatively slower compared to MongoDB.
Q: Which is easier to learn, MongoDB or MySQL?
MongoDB is easier to learn since it is designed with a modern approach and uses JavaScript as its query language. Whereas MySQL follows SQL query languages to perform the majority of the tasks.
Q: Will MongoDB replace MySQL?
Both unstructured and structured databases are used for different purposes. So, it is unlikely that MySQL will replace MongoDB.









 India
India USA
USA Australia
Australia Canada
Canada UK
UK UAE
UAE